17.3.1999 Mikko Kokkonen, 33015p
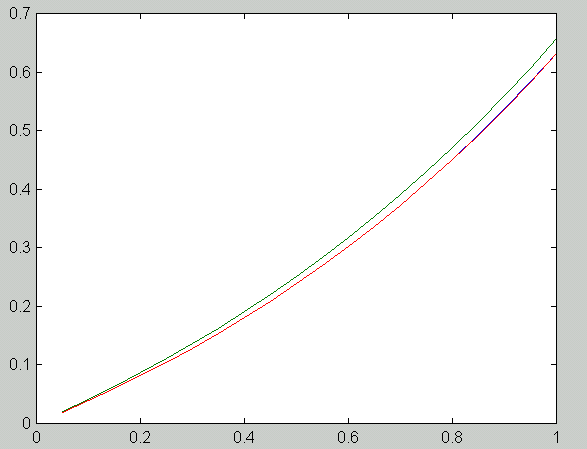
The image below shows the solutions of the boundary value problem. The blue curve is the true solution, the green curve is the numerical solution obtained with scheme 1 and the red curve is the solution obtained with scheme 2. Here n = 19.

Estimation of the rate of convergence (using the technique of Project 1.1 that has been implemented in a Matlab-script):
n h E_h1 E_h2 R_1 R_2
4.0000 0.2000 0.0946 0.0054
9.0000 0.1000 0.0486 0.0014 0.9592 1.9987
19.0000 0.0500 0.0247 0.0003 0.9800 1.9997
49.0000 0.0200 0.0099 0.0001 0.9910 1.9999
99.0000 0.0100 0.0050 0.0000 0.9961 2.0000
The scheme 2 converges faster because the two-sided finite difference
approximation of the first derivative is more accurate than the one-sided
(backward) approximation used in the scheme 1.
True Error
h error estimate
0.1000 0.0527 1.0417
0.0500 0.0137 0.2604
0.0250 0.0035 0.0651
0.0125 0.0009 0.0163
0.0062 0.0002 0.0041
The lesson of this exercise is that if the f'' has a large maximum value
compared to the average value of the function, then Theorem 2.2 can largely
overestimate the actual error.
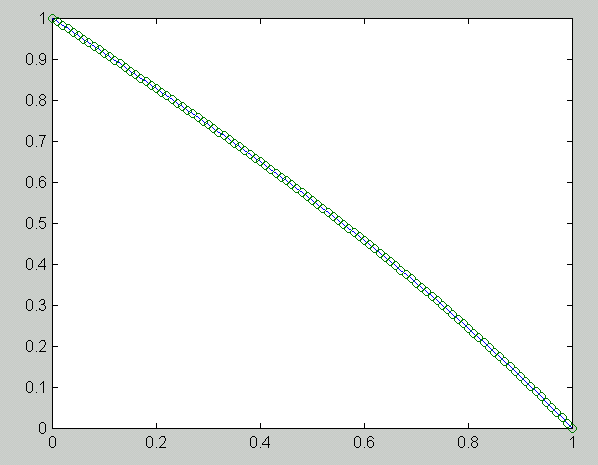
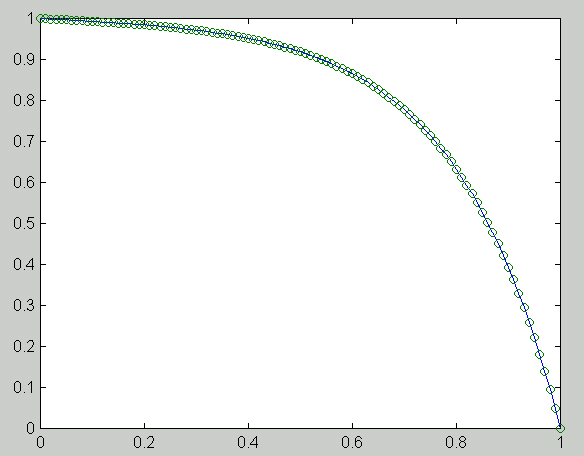
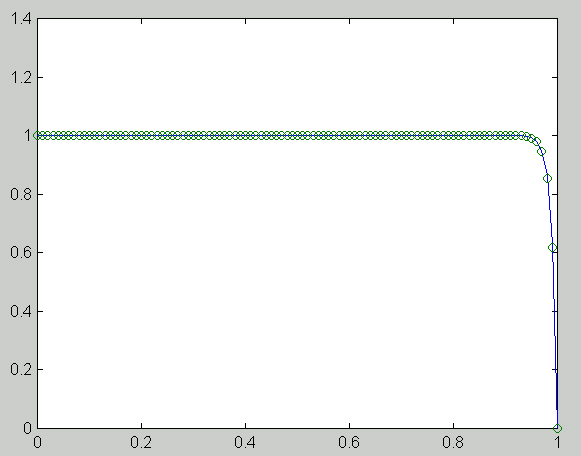
n h e_1 e_5 e_100 R_1 R_5 R_100
4 0.2000 0.0002 0.0140 0.0025
9 0.1000 0.0000 0.0037 0.0098 1.9946 1.9100 -1.9721
19 0.0500 0.0000 0.0010 0.0304 1.9986 1.9758 -1.6368
49 0.0200 0.0000 0.0002 0.0362 1.9997 1.9948 -0.1935
99 0.0100 0.0000 0.0000 0.0141 1.9993 1.9990 1.3632
199 0.0050 0.0000 0.0000 0.0037 2.0000 1.9998 1.9105
399 0.0025 0.0000 0.0000 0.0010 1.9999 1.9999 1.9759